2025
Performance Analysis of NOMA in SiPM-Based VLC Systems
Feiyu Jiao, Yansong Du, Yuting Zhou, Jingtong Yao, Qiang Jin, Bangyao Wang, Zhancong Xu, Juntian Qu, Xun Guan#
OptoElectronics and Communications Conference (OECC) 2025 Conference Poster
This work evaluates NOMA performance in SiPM-based VLC systems, considering nonlinearity and Poisson statistics. Results reveal that nonlinearity affects NOMA-OMA's achievable rate relative advantage; and optimal BER requires precise power allocation and ambient light control.

High-Sensitivity Refractive Index Sensor Based on Su-8 Polymer Micro-Ring Resonator
Yuting Zhou, Yuxuan Liu, Yansong Du, Feiyu Jiao, Jingtong Yao, Bangyao Wang, Simeng Li, Yutong Deng, Jian Song#, Xun Guan#
OptoElectronics and Communications Conference (OECC) 2025 Conference Poster
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a refractive index sensor based on SU-8 polymer micro-ring, which exhibits a sensitivity of 143.9 nm/RIU at a broad detection range of refractive index from 1.30 to 1.40.

A New Method for Removing Internal Scattering Noise in iToF Camera
Yansong Du, Jingtong Yao, Feiyu Jiao, Yuting Zhou, Qiang Jin, Bangyao Wang, Kang An, Zhaoxiang Jiang, Xun Guan#
Conference on Lasers and Electro-Optics Europe & European Quantum Electronics Conference (CLEO/Europe-EQEC) 2025 Conference Oral
We propose a novel solution to address internal scattering noise in iToF cameras based on wavelet decomposition and a multi-scale Point Spread Function. Theoretical analysis and experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which outperforms traditional approaches.

2024
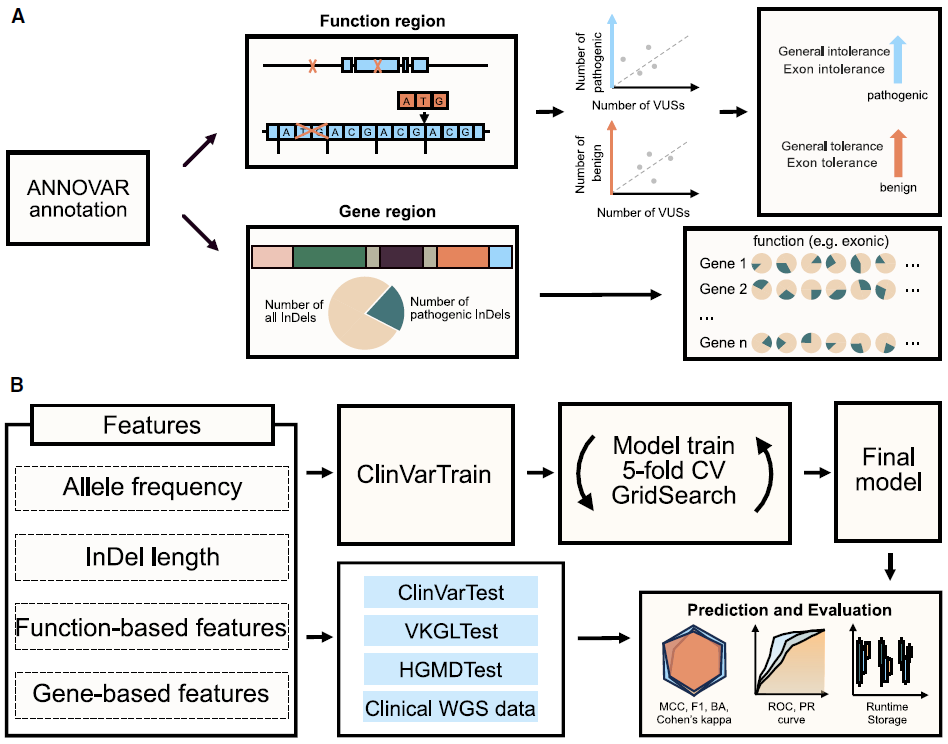
INDELpred: Improving the prediction and interpretation of indel pathogenicity within the clinical genome
Yilin Wei*, Tongda Zhang*, Bangyao Wang, Xiaosen Jiang, Mingyan Fang, Xin Jin, Yong Bai#
Human Genetics and Genomics Advances (HGG Advances) 2024 Journal
Small insertions and deletions (indels) are critical yet challenging genetic variations with significant clinical implications. In this paper, we developed INDELpred, a machine-learning-based predictive model for discerning pathogenic from benign indels. We envisage INDELpred as a desirable tool for the detection of pathogenic indels within large-scale genomic datasets, thereby enhancing the precision of genetic diagnoses in clinical settings.

2023
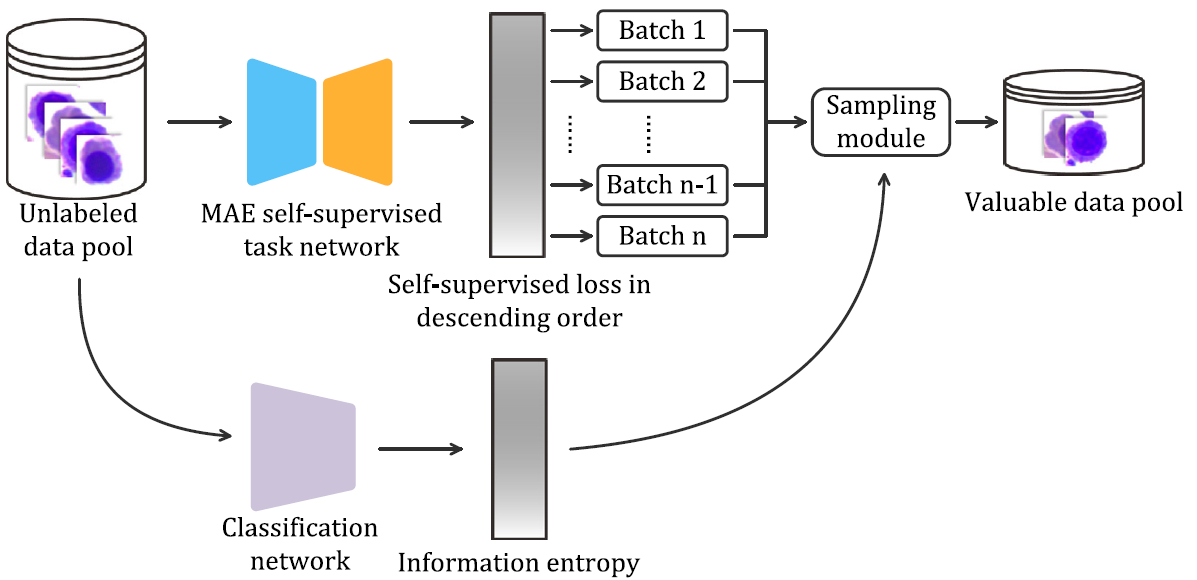
A blood cell classification method based on MAE and active learning
Qinghang Lu*, Bangyao Wang*, Quanhui He, Qingmao Zhang, Liang Guo, Jiaming Li, Jie Li, Qiongxiong Ma#
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 2023 Journal
Cell morphology analysis is a crucial diagnostic tool for identifying blood diseases. This paper proposes a blood cell classification method based on Masked Autoencoder (MAE) and active learning (AL) to select the most valuable samples for labeling. The proposed approach achieves comparable classification performance to SOTA method based on ResNeXt when utilizing only 20% of the labeled data.

Marks: * equal contribution, # corresponding author